When delivering projects successfully and consistently, two roles stand out as critical: the Project Management Office (PMO) and the Project Manager. While each has its responsibilities and focus, they are deeply interconnected, both share software tools, data, and a unified goal of driving project success. In this blog, we’ll explore both roles, how they complement each other, and how Jira helps them operate more effectively.
It’s important to note that the Project Manager focuses on the day-to-day execution of the projects, tracking tasks, managing timelines, and ensuring team alignment, and the PMO operates at a strategic and organizational level, this role is responsible for defining standards, maintaining governance, and providing visibility across all projects.
To get a better overview of both roles, think of the Project Manager as the driver of a single vehicle, while the PMO oversees traffic flow across the entire fleet. To succeed, they need shared access to reliable, up-to-date project data, which in this case will be in Jira. Let’s get into the details about their roles:
What’s the role of a Project Manager Office (PMO)?
Also known by its initials, the PMO is a crucial organizational entity that standardizes and improves project management practices. It’s the central hub that oversees and supports all project-related activities within an organization.
9 Project Manager Office key functions:
- Establishing standards and methodologies: The PMO develops and maintains project management methodologies, standards, processes, and best practices, ensuring consistency across all projects within an organization. As you can see in this real-life example.
- Provide guidance and support: They support project managers with mentoring, training, and expertise on project management solutions and techniques. They're the central contact for project-related queries and issues.
- Resource Management: The PMO often oversees the allocation and management of resources across different projects. This involves ensuring that the right resources (human, financial, and material) are assigned to the right projects at the right time, optimizing resource utilization, and avoiding conflicts.
- Project Portfolio Management: Managing the organization's portfolio of projects is key. This includes prioritizing projects based on strategic alignment, assessing their potential and risks, and monitoring their overall progress to ensure they contribute to organizational goals.
- Monitoring and controlling projects: The PMO establishes mechanisms for tracking project progress, performance, and metrics. They generate reports and dashboards to provide visibility to stakeholders, identify potential issues, and ensure projects stay on track in terms of scope, schedule, and budget.
- Risk and Issue management: The PMO often plays a role in establishing risk management frameworks and processes. They may help project teams identify, assess, and mitigate risks, as well as track and resolve issues that arise during project execution.
- Knowledge Management: The PMO serves as a repository for project documentation, lessons learned, and best practices. This knowledge base can be leveraged for future projects, improving efficiency and reducing the likelihood of repeating mistakes.
- Ensuring strategic alignment: They ensure that projects align with the organization's strategic goals and objectives by selecting and prioritizing projects that will deliver the most value and contribute to the overall business strategy.
- Improving project management maturity: They're actively enhancing the organization's project management capabilities over time by introducing best practices and fostering a continuous improvement culture.
Then, why is it beneficial to have a PMO within an organization?
Having a Project Management Office within your organization helps to align projects by following strategic business objectives, ensuring consistency in execution across the organization. A PMO establishes standardized processes, tools, and governance that improve efficiency, reduce risks, and enhance visibility into project performance.
Ultimately, a well-functioning PMO acts as a central hub that supports informed decision-making and drives organizational maturity in project management. More specifically, it helps to:
- Achieve improved project success rates by standardizing processes and providing support. Contributing to complete projects on time, within budget, and to the required quality.
- Enhance efficiency and consistency by applying standardized methodologies and software solutions, leading to more efficiency in project execution.
- Ensure better resource allocation by centralizing resource management and reducing conflicts.
- Increases transparency and accountability through regular reporting, providing stakeholders with clear project progress visibility.
- Improves decision-making by granting access to accurate reporting of project data, enabling project managers and management.
- Enhances strategic alignment, ensuring that projects are aligned with organizational goals, maximizing the return on investment in project initiatives.
- Reduce risks and issues in project development by performing proactive management of risks and resolving issues, minimizing potential negative impacts on projects.
- Sharing lessons learned, leading to continuous improvement in project management practices across the organization.
In essence, the PMO acts as a central authority and support system for project management within an organization, driving efficiency, consistency, and ultimately contributing to the successful delivery of projects that align with strategic objectives. As you can see in this case, within the hospitality industry.
What’s the role of a Project Manager?
Ah, the project manager! If the PMO oversees the traffic and provides the guidelines on how to drive, the project manager is the conductor of a single vehicle, which would be an individual project. They are directly responsible for planning, executing, and closing a specific project to achieve its defined goals and objectives.
11 Project Manager Office key functions:
- Project initiation and planning: The Project Manager defines the project's objectives, scope, and deliverables in collaboration with involved stakeholders by developing a plan that outlines tasks, timelines, resources, budget, and potential risks. This often involves creating work breakdown structures (WBS), Gantt charts, and other planning tools.
- Team leadership and management: They build and lead the project team, assigning tasks, setting expectations, and motivating team members. This includes fostering effective communication, resolving conflicts, and ensuring the team works collaboratively towards the project goals.
- Project execution and progress monitoring: They oversee the day-to-day execution of the project, ensuring tasks are completed according to the plan, monitoring progress, tracking established milestones, managing budget and costs, and addressing any deviations.
- Stakeholder management: Managing the project communication and relationships with people involved in the project is crucial, keeping them informed about progress.
- Risk and issues management: They proactively identify potential risks and mitigate them by implementing accurate strategies to find solutions and minimize their impact on the project.
- Budget management: They are responsible for managing the project budget, tracking expenses and costs, ensuring the project stays within the allocated financial resources, often forecasting costs, and managing change requests that may impact the budget.
- Schedule management: They develop and maintain the project schedule, ensuring tasks are completed on time and the project meets its deadlines. Tracking progress against the schedule, identifying potential delays, and implementing corrective actions.
- Quality assurance: They ensure that project deliverables meet the required quality standards, sometimes implementing quality control processes and conducting reviews or testing.
- Communication and reporting: They are the central point of communication for project matters, regularly reporting about project status, risks, and issues to stakeholders.
- Change management: As projects often encounter changes in scope or requirements, project managers need to undertake these changes through a defined process, assessing their impact and obtaining necessary approvals.
- Project closure: Once project deliverables are complete, the project manager formally closes the project, involving documentation, stakeholders' sign-off, post-project reviews to identify lessons learned, and releasing resources.
As we can see, Project Managers need a specific set of skills to undertake those responsibilities and lead projects effectively from start to finish:
Strong leadership is essential to motivate and guide the team, and excellent communication helps to engage with stakeholders. Planning abilities ensure task prioritization, and problem-solving skills are necessary to address challenges.
Also, counting on effective negotiation skills increases interest alignment and time management keeps the project on track, following milestones, and sticking to project timelines. Another skill is a solid understanding of budget management and cost control, alongside risk management knowledge to anticipate and mitigate potential setbacks.
In essence, the Project Manager is the driving force behind a specific project's success. They are responsible for the "how" of getting the project done, ensuring that the team works effectively, resources are managed efficiently, and the project delivers the intended outcomes.
They work closely with the PMO, often adhering to the standards and methodologies established by them, while focusing on the successful delivery of their assigned project.
How do both of these roles use Jira?
Natively, Jira is a powerful tool that both the PMO and Project Managers utilize, they often leverage its features in slightly different ways to achieve their respective goals. Think of it like a shared workspace with different levels of access and focus.
Most common ways Project Managers use Jira:
For a Project Manager, Jira is their day-to-day project execution and team collaboration software tool. They use it extensively for:
- Task management & tracking: Creating, assigning, and tracking individual tasks and sub-tasks required to deliver project outcomes. This also includes assigning responsibility, setting priorities, and monitoring resolution.
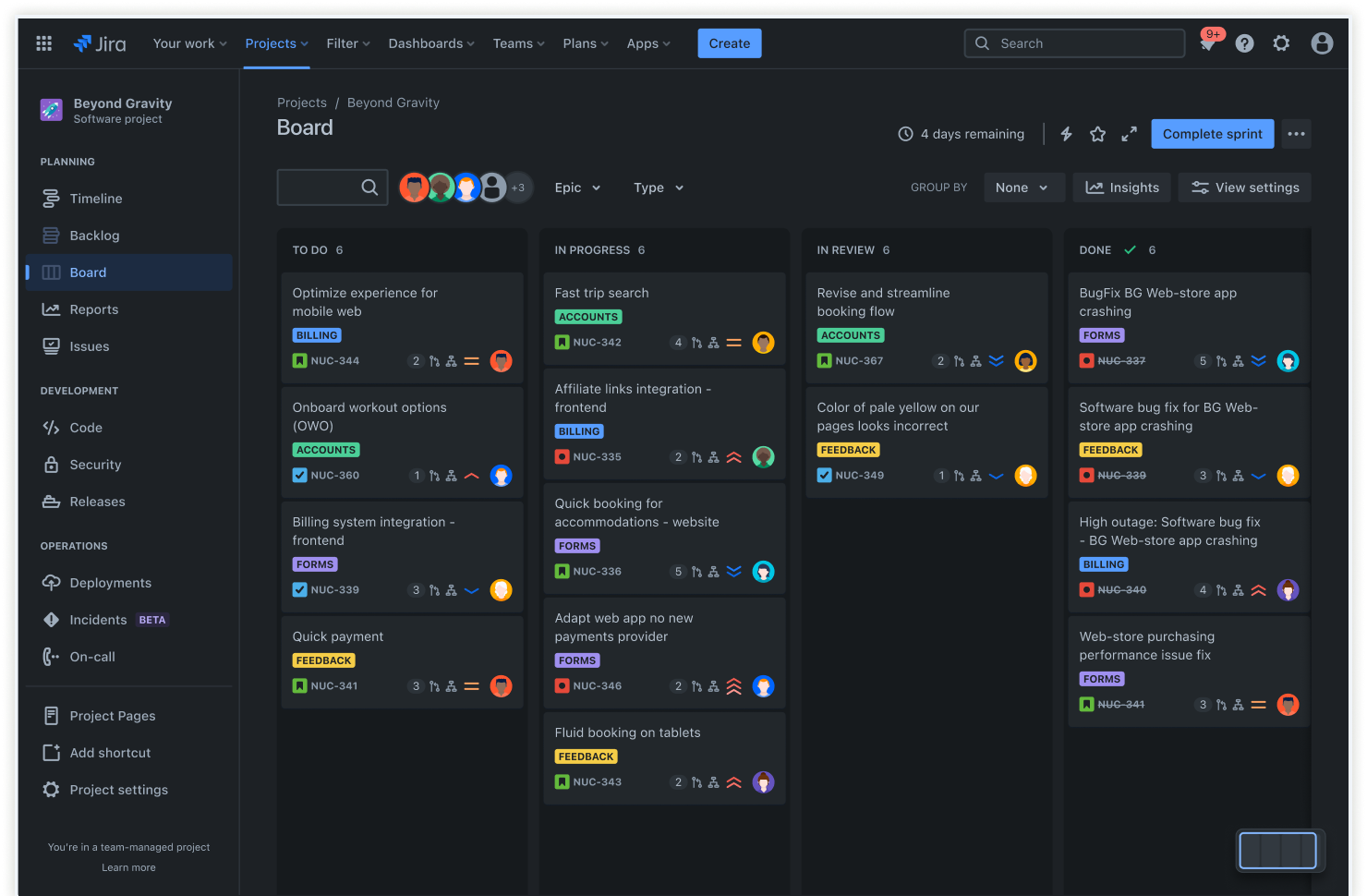
Jira's Scrum Board (dark mode)
- Sprint planning & backlog management (in Agile environments): Defining and managing sprints, creating and grooming user stories and tasks within sprints, estimating effort, tracking sprint burndown, maintaining and prioritizing the project backlog, and planning future iterations.
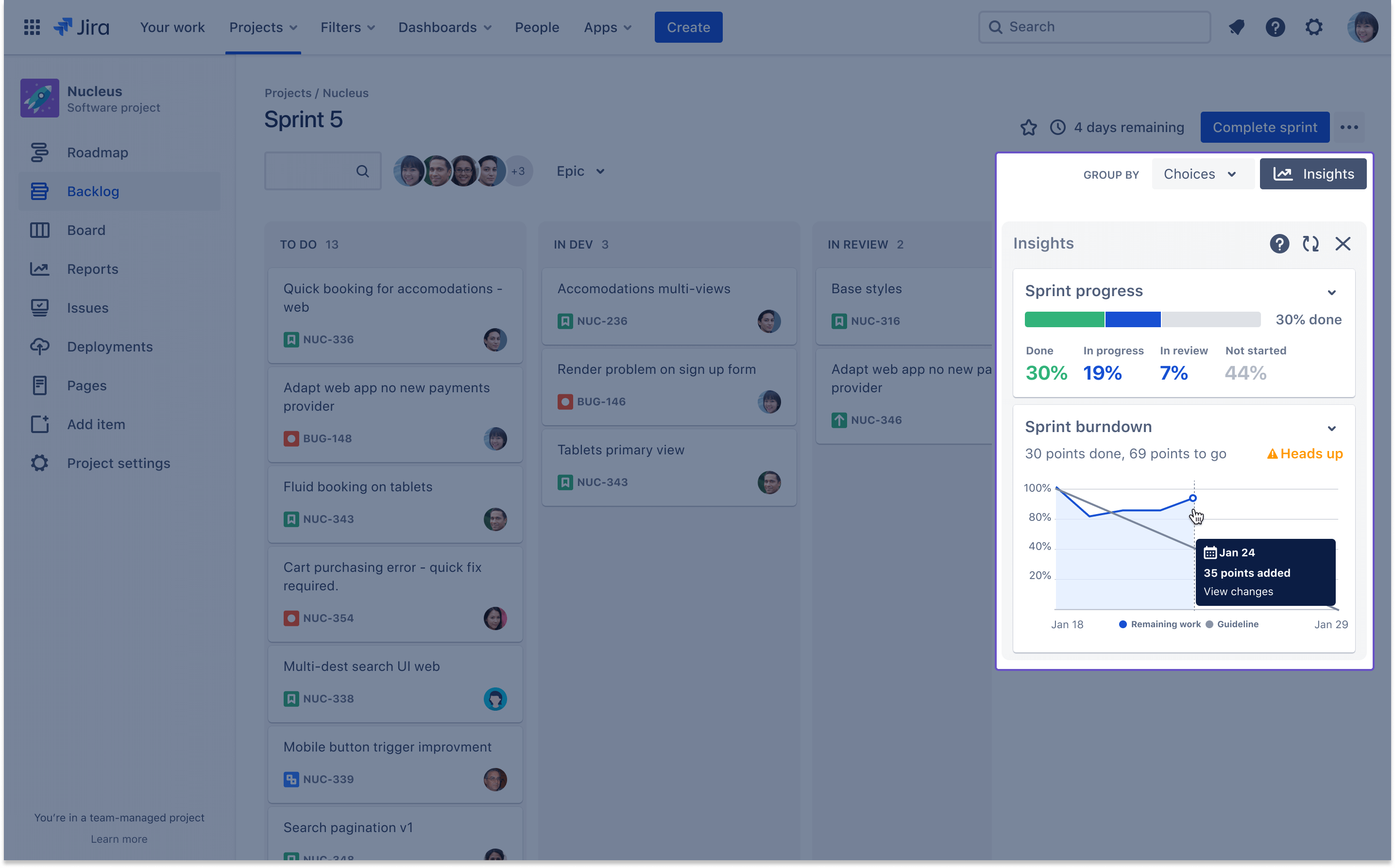
An example of how Jira provides reports for Project Managers.
- Workflow management: Jira's customizable workflows allow them to define the stages a work item goes through, ensuring a consistent and transparent process.
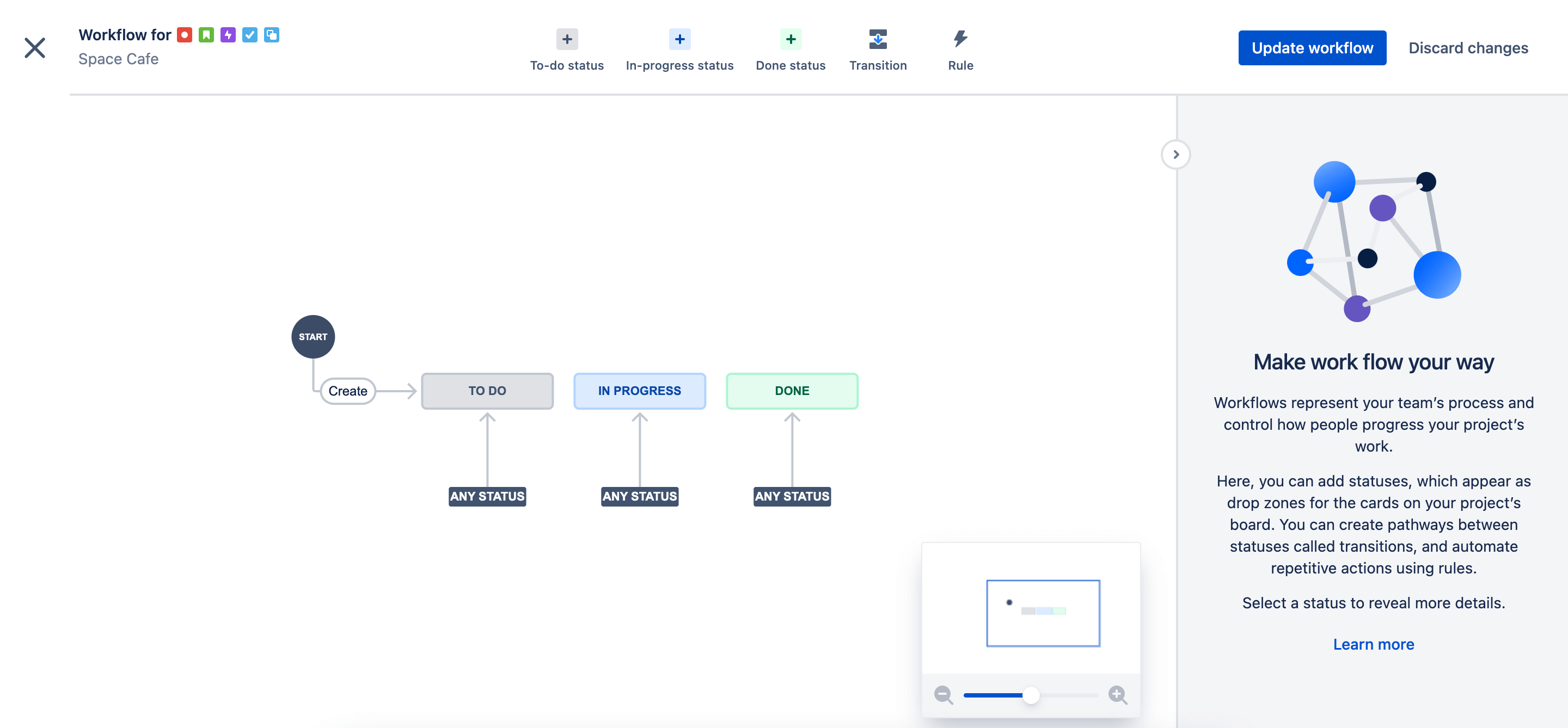
Jira allows you to create, visualize, and edit the steps and transitions of a workflow.
- Collaboration and communication: Commenting on tasks and issues, mentioning team members, and sharing files to facilitate communication and keep everyone informed.
- Progress visualization: Using Jira dashboards and reports to visualize task progress, tracking key metrics on burndown charts, velocity charts, and similar to identify potential roadblocks.
- Reporting: Generating reports on task status, issue resolution, team performance, and overall project progress to keep stakeholders informed.
In essence, the Project Manager uses Jira as their central command center for a specific project, focusing on the granular details of execution and team coordination.
Common ways PMOs take advantage of Jira
The PMO takes a more strategic view of the data of the projects within Jira. Natively, their usage of Jira is often complemented by solutions available in the Atlassian Marketplace:
- Standardization and governance: Natively, Jira responds to projects from a task perspective; that way, they need to configure Jira to enforce organizational project management standards and workflows to respond to multiple projects. This is a large configuration, ensuring how projects are managed and reported.
- Portfolio management: Utilizing Jira Align to get a high-level view of all active projects, their status, risks, and resource allocation. This helps in strategic decision-making and portfolio optimization.
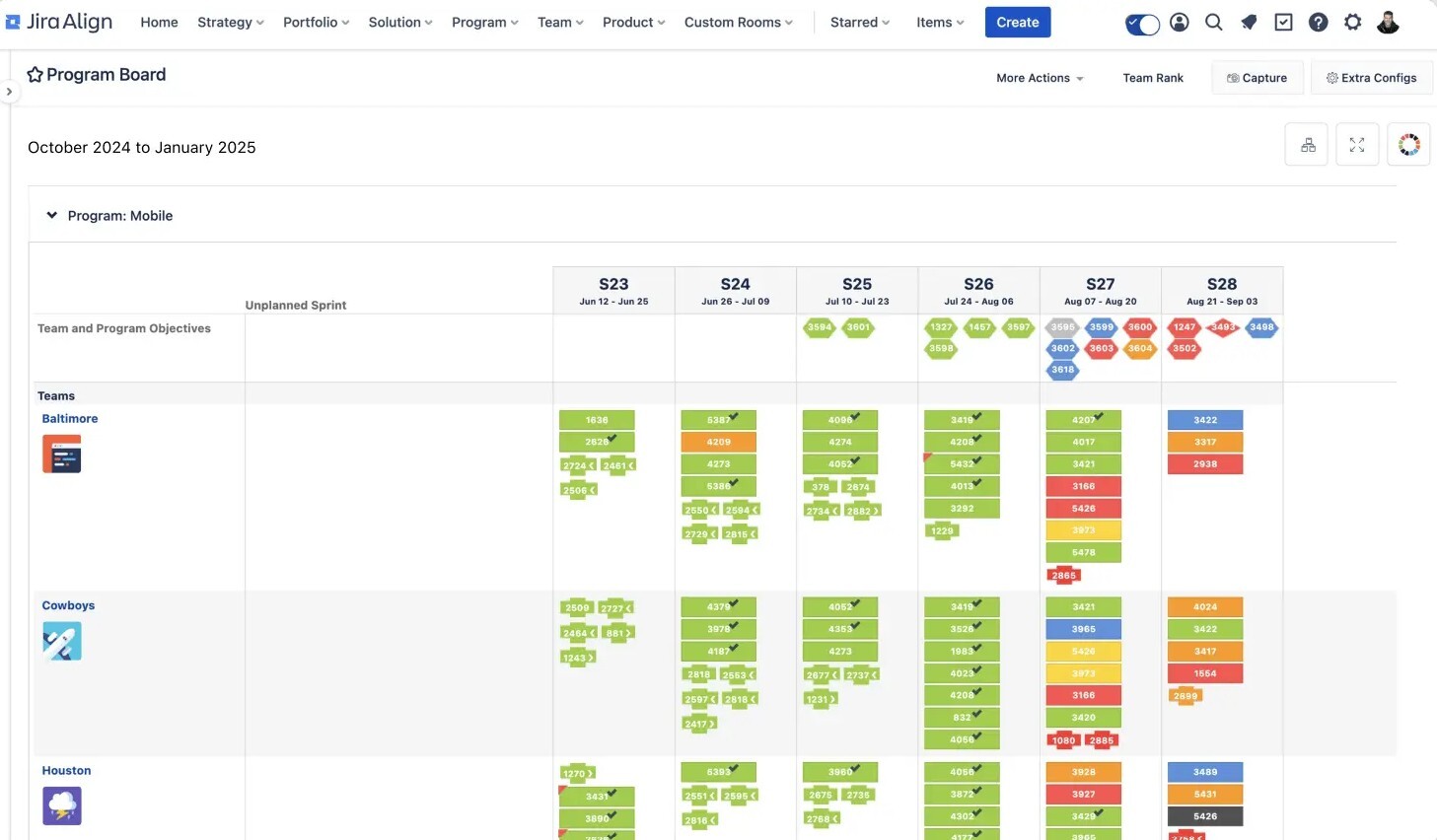
Jira Align is great for deploying the right team to choose which project to focus on next.
- Reporting and analytics: Aggregating task-based data from multiple Jira projects helps them to identify trends, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement across their projects. They might create dashboards on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for the PMO.
 Natively, Jira offers different ready-to-use reports at the task level, accessible for all Jira projects.
Natively, Jira offers different ready-to-use reports at the task level, accessible for all Jira projects.
- Managing & standardizing workflows: Creating and managing workflows in Jira that project managers can use to ensure consistency across projects.
- Compliance and auditing: Using Jira's history and audit logs to ensure projects are following established processes and meeting compliance requirements.
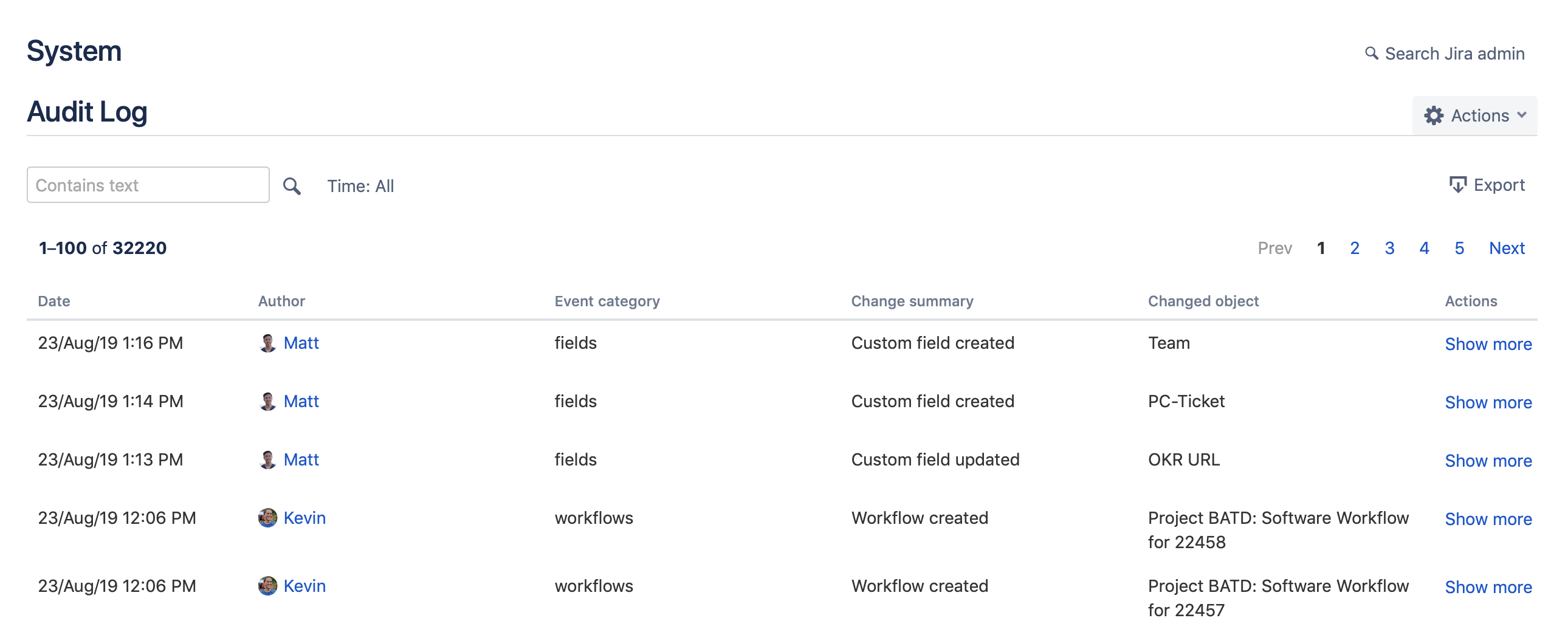
Jira Audit logs track key activities in Jira that can be viewed in the Jira administration console.
- Administering & managing organizational knowledge: Analyzing data from completed projects in Jira to identify lessons learned and best practices that can be incorporated into organizational standards and future projects. For this, it’s usually also used a wiki as Confluence.
In essence, the PMO uses Jira as a data hub to gain visibility across the entire project landscape, enforce standards, track portfolio performance at a task level, and drive continuous improvement in project management practices.
It's important to note that the Project Manager and the PMO often work collaboratively within Jira. Project Managers provide the detailed and operational project data that the PMO then aggregates and analyzes. The PMO, in turn, might provide Jira with the help of means from the Atlassian Marketplace in ways that support project managers by providing standardized workflows and reporting structures.
How do PMOs and Project Managers use Projectrak for Jira?
Projectrak, concerning both the PMO and individual Project Managers, builds upon the foundation that Jira provides, granting a layer over it, allowing to building a project portfolio with Jira data, and adding more project data from the very first minute the solution is acquired.
Projectrak enhances the experience for both roles, complementing what Jira offers:
4 Ways Projectrak helps the PMO:
Jira, in its native form, excels at managing individual work items (issues). As a PMO needs to look at the bigger picture, it can be challenging to get a consolidated view of project health and portfolio performance. Projectrak steps in to bridge this gap by:
1. Providing a project portfolio visibility:
- Jira: Offers visibility into individual issues and their status within a project.
- Projectrak: Adds a layer of visibility at the project level. The PMO can see key project metrics (status, priorities, stakeholders, etc.) across all projects at a single glance (through different views and dashboards). This eliminates the need to navigate into each project individually.
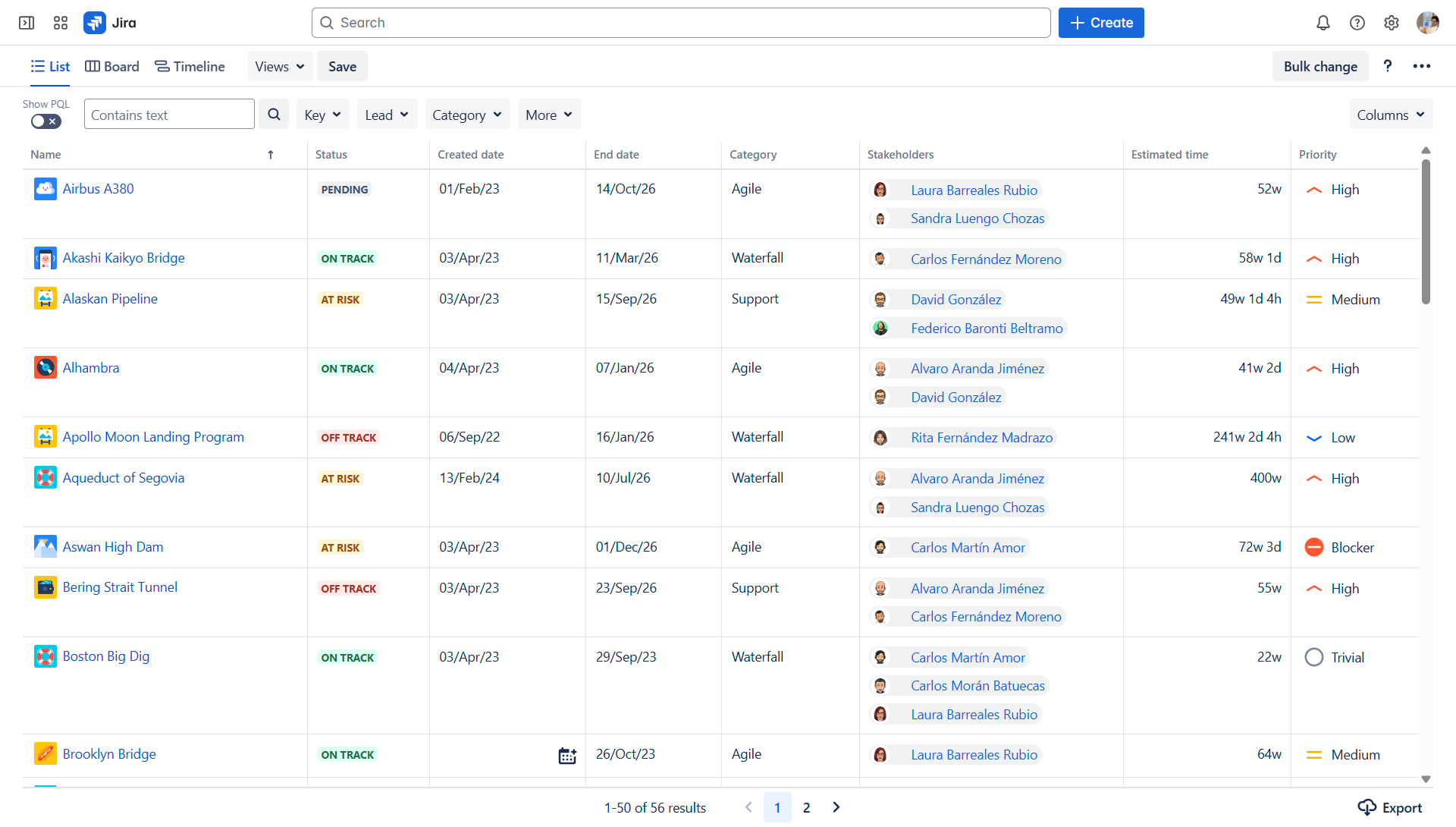
Projectrak's List view offers an overall project portfolio overview.
2. Enforcing project standards and governance:
- Jira: Allows the workflow standardization at the issue level.
- Projectrak: Enables the PMO to define and track adherence to project-level standards and governance. They can ensure consistent data capture (e.g., mandatory project status fields) across all projects, facilitating consistent reporting and analysis.
3. Enhanced portfolio reporting and analytics:
- Jira: Offers reporting on issues within a project.
- Projectrak: Allows the PMO to create aggregated reports and dashboards based on the custom project-level fields. This provides insights into the overall health of the project portfolio, identifies trends, and supports data-driven decision-making (e.g., which projects are at risk, where resources might be needed).
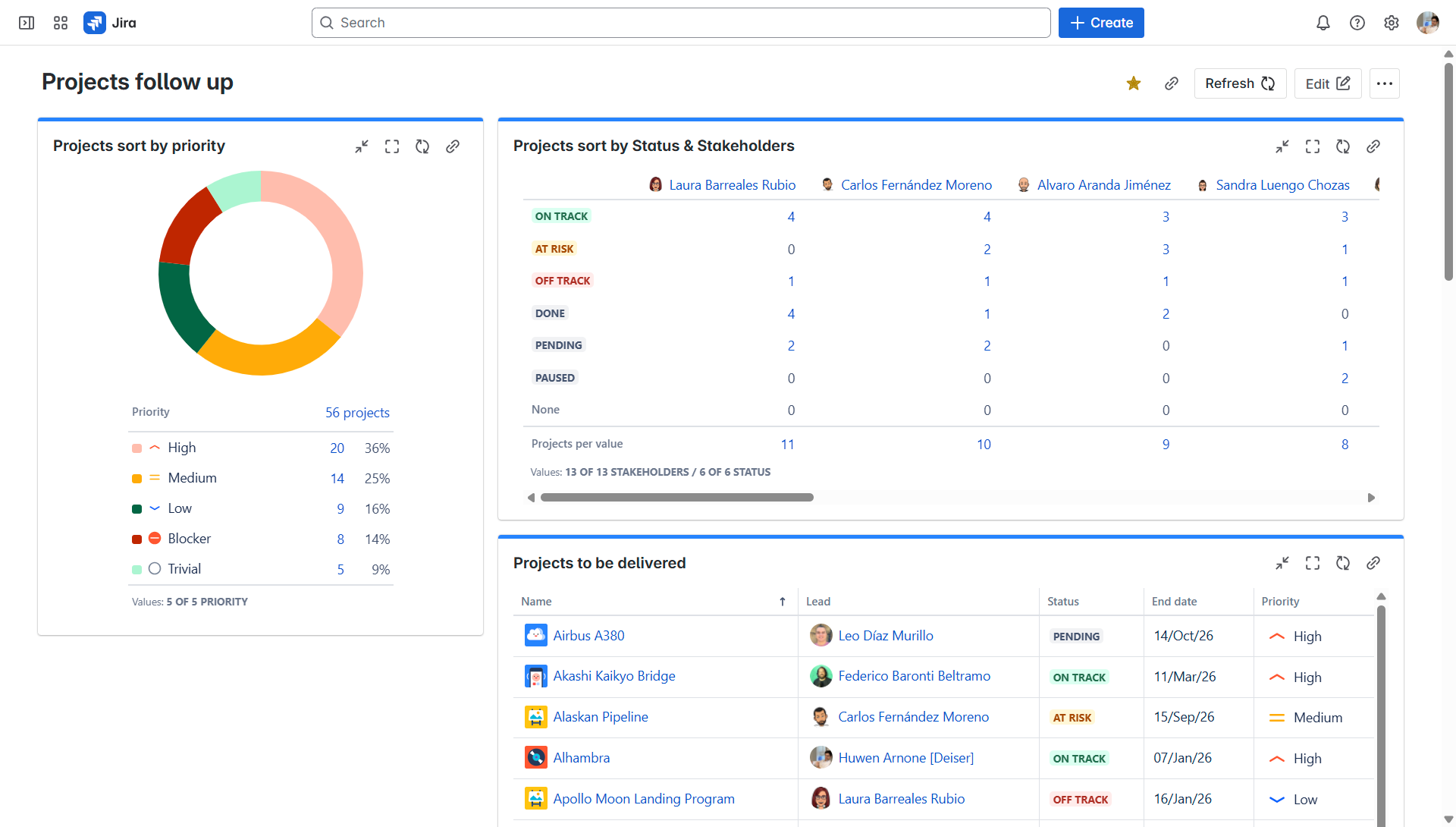
You can configure Jira Dashboards with Projectrak gadgets to get project reporting in shape.
4. Strategic alignment tracking:
- Jira: Focuses on task completion.
- Projectrak: Allows the PMO to track the strategic alignment of each project by capturing relevant data (e.g., strategic goals supported, business value). This ensures the portfolio is aligned with organizational objectives.
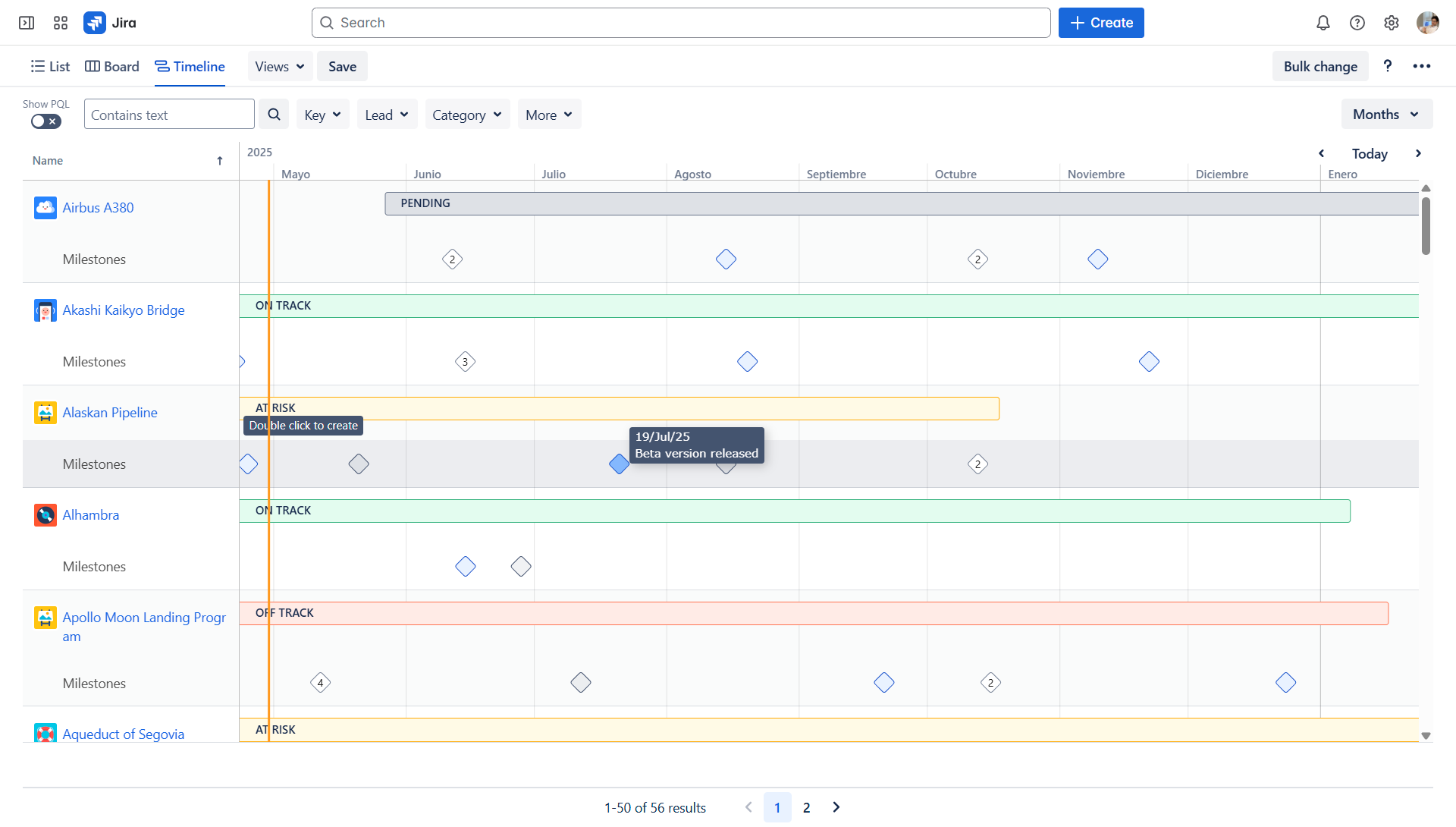
Projectrak's Timeline view allows you to see the point in time and project progress, besides establishing key project milestones for projects.
Projectrak empowers the PMO to move beyond managing individual tasks to managing the portfolio of projects as a cohesive entity within Jira.
4 Ways Projectrak helps the Project Managers:
As Projectrak offers a wider overview of projects, it’s also beneficial for Project Managers, as they primarily work within individual Jira projects; their experience is enhanced because they get:
A holistic project overview:
- Jira: Focuses on issue-level details.
- Projectrak: Offers a dedicated space within Jira of the project to view and manage key project-level information. This provides a quick summary of the project's health, status, and critical data points without having to piece it together from various issues.
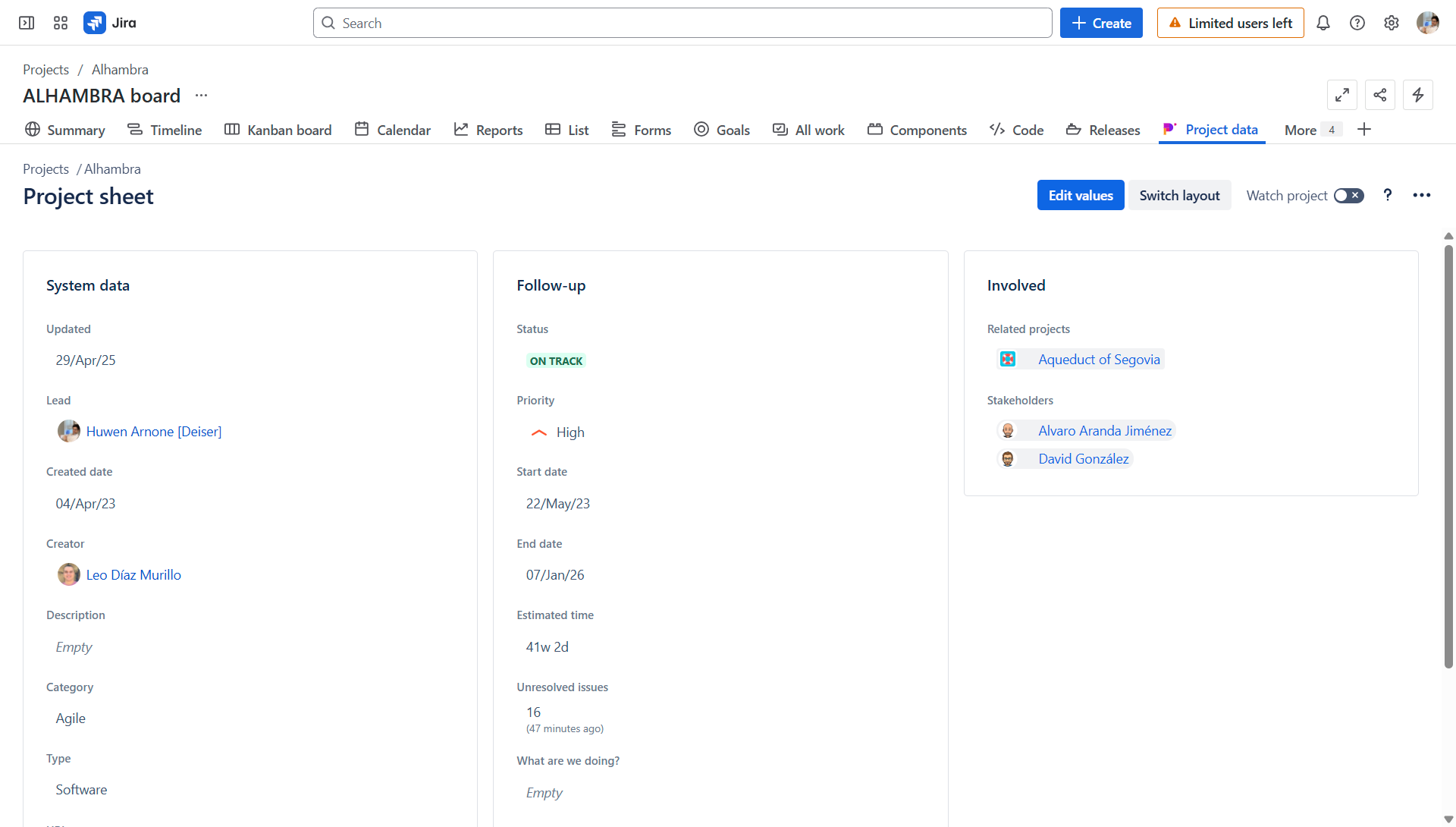
The predefined Project sheet, Projectrak, allows for centralizing and controlling specific project data.
Improved stakeholder communication:
- Jira: Communication often revolves around specific tasks or issues.
- Projectrak: Makes it easier for Project Managers to communicate high-level project status and key metrics to stakeholders through readily available project overviews, email notifications, and reports based on the project-level data.
Simplified reporting:
- Jira: Generating comprehensive project reports can sometimes require complex JQL queries or the use of other reporting apps.
- Projectrak: Simplifies reporting by allowing Project Managers to easily generate reports based on specific gadgets that allow to display of project-level information, enabling quick updates on project status, priorities, and other key information.
Better organization of project-specific data:
- Jira: Project-specific information might be scattered across various issues and even in the wiki (Confluence).
- Projectrak: Provides structured ways (views) to organize and display key project information directly within the Jira project, making it easily accessible to the entire team according to a specific need.
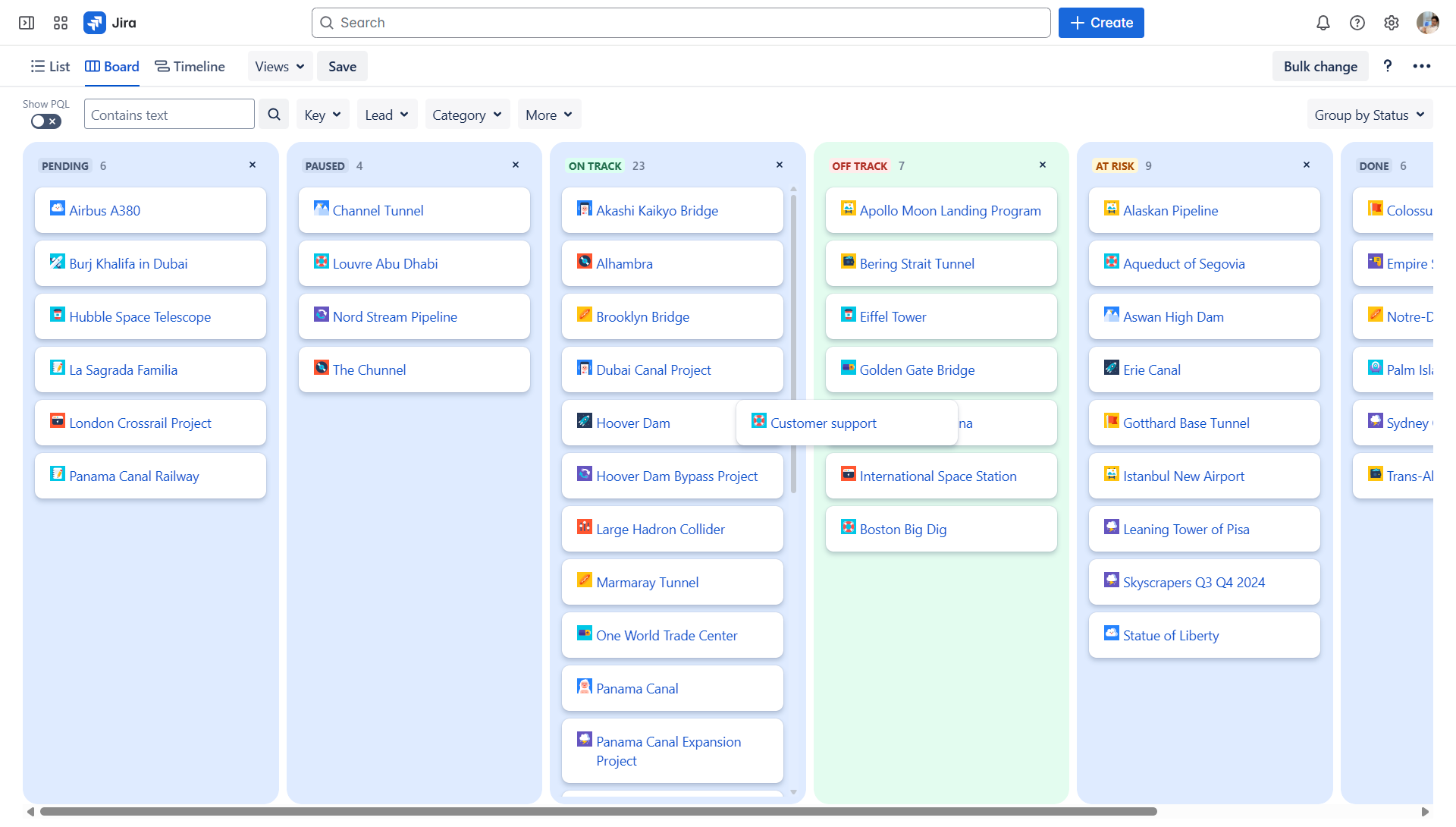
Projectrak Board view allows communication of specific project attributes, such as status or priorityenhancing structure
and stakeholder communication.
Projectrak provides Project Managers with a more structured and efficient way to manage and communicate key project-level information within their Jira projects, aligning with the broader portfolio view of the PMO.
The synergistic effect within enterprise projects
The real power of Jira and Projectrak comes from their synergy. Jira provides a robust engine for task management, while Projectrak adds the crucial layer for managing and reporting on projects as strategic entities. This allows the PMO to have the portfolio-level insights they need for strategic decision-making and management, while empowering Project Managers with better tools for managing and communicating the health of their projects within the same familiar Jira environment. The consistent data captured at the project level by Project Managers directly feeds into the portfolio-level views and reports used by the PMO.
A successful project solution doesn’t just happen, it’s built based on the needs, organized with structure, clarity, and collaboration. The PMO provides the strategic foundation, setting standards and offering oversight, while the Project Manager brings that vision to life on the ground. Together, and with the support of tools like Jira and Projectrak, they transform complexity into progress. Whether you're managing one project or an entire portfolio, understanding how these roles interact is key to driving results and achieving lasting impact.





 Natively, Jira offers different ready-to-use reports at the task level, accessible for all Jira projects.
Natively, Jira offers different ready-to-use reports at the task level, accessible for all Jira projects.






No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think